This blog post series is on machine learning with R. We will use the Caret package in R. In this part, we will first perform exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) on a real-world dataset, and then apply non-regularized linear regression to solve a supervised regression problem on the dataset. We will predict power output given a set of environmental readings from various sensors in a natural gas-fired power generation plant.
In the second part of the post, we will work with regularized linear regression models (ridge, lasso and elasticnet). Next, we will see the other non-linear regression models. The real-world data we are using in this post consists of 9,568 data points, each with 4 environmental attributes collected from a Combined Cycle Power Plant over 6 years (2006-2011), and is provided by the University of California, Irvine at UCI Machine Learning Repository Combined Cycle Power Plant Data Set. You can find more details about the dataset on the UCI page. The task is a regression problem since the label (or target) we are trying to predict is numeric.
Libraries
The caret package (short for _C_lassification _A_nd _RE_gression _T_raining) is a set of functions that attempt to streamline the process for creating predictive models.
library(readxl) library(ggplot2) library(corrplot) library(tidyverse)
Load Data
power_plant = read_excel("Folds5x2_pp.xlsx")
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
This is a step that we should always perform before trying to fit a model to the data, as this step will often lead to important insights about our data.
class(power_plant) 'tbl_df' 'tbl' 'data.frame'
# Caret faces problems working with tbl,
# so let's change the data to simple data frame
power_plant = data.frame(power_plant)
message("The class is now ", class(power_plant))
# See first few rows
head(power_plant)
AT V AP RH PE
14.96 41.76 1024.07 73.17 463.26
25.18 62.96 1020.04 59.08 444.37
5.11 39.40 1012.16 92.14 488.56
20.86 57.32 1010.24 76.64 446.48
10.82 37.50 1009.23 96.62 473.90
26.27 59.44 1012.23 58.77 443.67
The columns in the DataFrame are:
- AT = Atmospheric Temperature in C
V = Exhaust Vacuum Speed
AP = Atmospheric Pressure
RH = Relative Humidity
PE = Power Output
Power Output is the value we are trying to predict given the measurements above.
# Size of DataFrame dim(power_plant) 9568 5
map(power_plant, class) # all columns are numeric $AT 'numeric' $V 'numeric' $AP 'numeric' $RH 'numeric' $PE 'numeric'
Are there any missing values in any of the columns?
map(power_plant, ~sum(is.na(.))) # using purrr package # There is no missing data in all of the columns $AT 0 $V 0 $AP 0 $RH 0 $PE 0
Visualize relationship between variables
Before we perform any modeling, it is a good idea to explore correlations between the predictors and the predictand. This step can be important as it helps us to select appropriate models. If our features and the outcome are linearly related, we may start with linear regression models. However, if the relationships between the label and the features are non-linear, non-linear ensemble models such as random forest can be better.
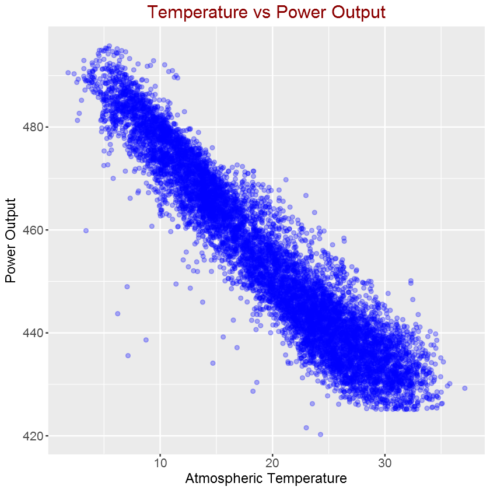
Correlation between atmospheric temperature and power output
power_plant %>% ggplot(aes(AT, PE)) +
geom_point(color= "blue", alpha = 0.3) +
ggtitle("Temperature vs Power Output") +
xlab("Atmospheric Temperature") +
ylab("Power Output") +
theme(plot.title = element_text(color="darkred",
size=18,hjust = 0.5),
axis.text.y = element_text(size=12),
axis.text.x = element_text(size=12,hjust=.5),
axis.title.x = element_text(size=14),
axis.title.y = element_text(size=14))
As shown in the above figure, there is strong linear correlation between Atmospheric Temperature and Power Output.
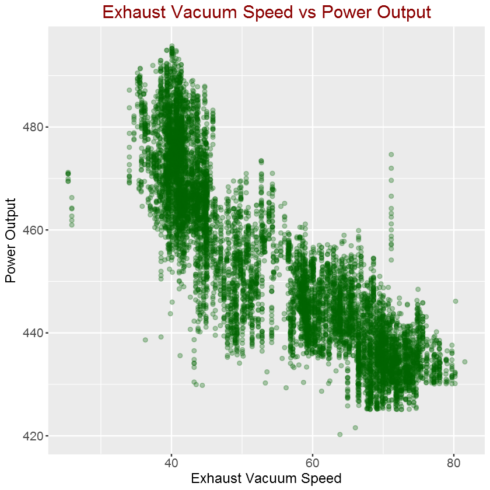
Correlation between Exhaust Vacuum Speed and power output
power_plant %>% ggplot(aes(V, PE)) +
geom_point(color= "darkgreen", alpha = 0.3) +
ggtitle("Exhaust Vacuum Speed vs Power Output") +
xlab("Exhaust Vacuum Speed") +
ylab("Power Output") +
theme(plot.title = element_text(color="darkred",size=18,hjust = 0.5),
axis.text.y = element_text(size=12),
axis.text.x = element_text(size=12,hjust=.5),
axis.title.x = element_text(size=14),
axis.title.y = element_text(size=14))
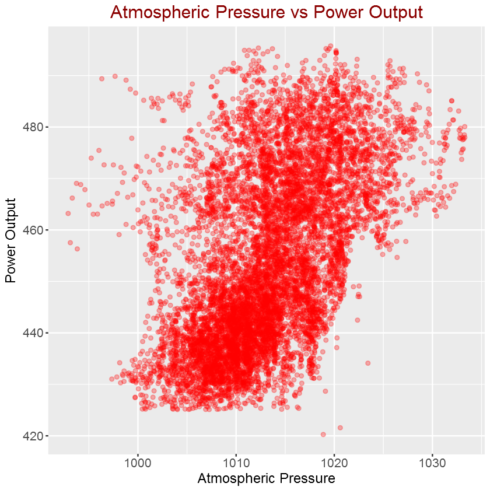
Correlation between atmospheric pressure and power output
power_plant %>% ggplot(aes(AP, PE)) +
geom_point(color= "red", alpha = 0.3) +
ggtitle("Atmospheric Pressure vs Power Output") +
xlab("Atmospheric Pressure") +
ylab("Power Output") +
theme(plot.title = element_text(color="darkred",size=18,hjust = 0.5),
axis.text.y = element_text(size=12),
axis.text.x = element_text(size=12,hjust=.5),
axis.title.x = element_text(size=14),
axis.title.y = element_text(size=14))
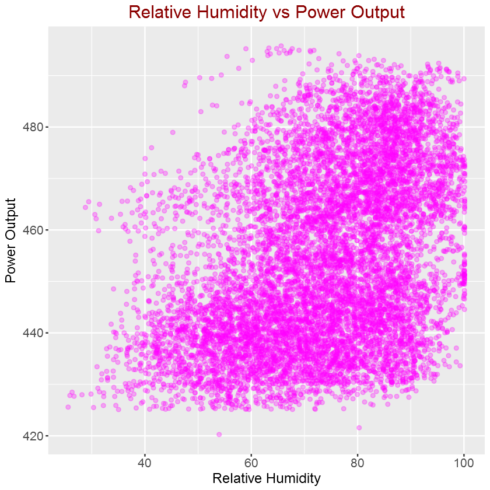
Correlation between relative humidity and power output
power_plant %>% ggplot(aes(RH, PE)) +
geom_point(color= "magenta", alpha = 0.3) +
ggtitle("Relative Humidity vs Power Output") +
xlab("Relative Humidity") +
ylab("Power Output") +
theme(plot.title = element_text(color="darkred",size=18,hjust = 0.5),
axis.text.y = element_text(size=12),
axis.text.x = element_text(size=12,hjust=.5),
axis.title.x = element_text(size=14),
axis.title.y = element_text(size=14))
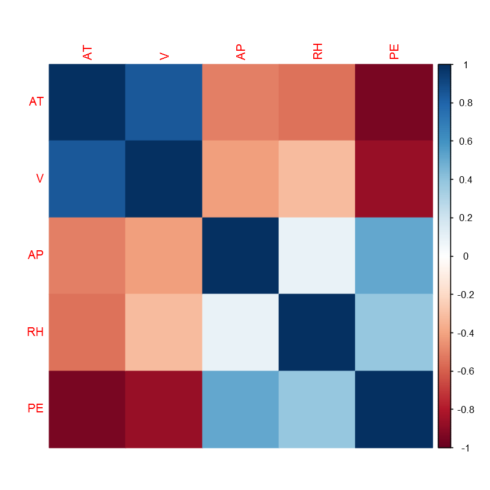
Correlation heatmap
correlations = cor(power_plant) corrplot(correlations, method="color")
As shown in the correlation heatmap above, the target is correlated with the features. However, we also observe correlation among the features, hence we have multi-collinearity problem. He will use regularization to check if the collinearity we observe has a significant impact on the performance of linear regression model.
Data Modeling
All the columns are numeric and there are no missing values, which makes our modeling task straightforward. Now, let’s model our data to predict what the power output will be given a set of sensor readings. Our first model will be based on simple linear regression since we saw some linear patterns in our data based on the scatter plots and correlation heatmap during the exploration stage. We need a way of evaluating how well our linear regression model predicts power output as a function of input parameters. We can do this by splitting up our initial data set into a Training Set, used to train our model and a Test Set, used to evaluate the model’s performance in giving predictions.
library(caret) # Caret streamlines the process for creating predictive models. # The package contains tools for: # data splitting # pre-processing # feature selection # model tuning using resampling # variable importance estimation # as well as other functionality.
The Caret createDataPartition function creates indices for training and test portion of the data for us.
# create training set indices with 80% of data
set.seed(100) # For reproducibility
# Create index for testing and training data
inTrain <- createDataPartition(y = power_plant$PE,
p = 0.8, list = FALSE)
# subset power_plant data to training
training <- power_plant[inTrain,]
# subset the rest to test
testing <- power_plant[-inTrain,]
# Size ratio of training and test dataset
message("As shown below, the training set is about 80% and the test set is about 20% of the original data")
rbind("Training set" = nrow(training)/nrow(power_plant),
"Testing set" = nrow(testing)/nrow(power_plant)) %>%
round(2)*100
Training set 80
Testing set 20
As shown above, the training set is about 80% and the test set is about 20% of the original data
Linear Regression
# Fit linear regression model
# put the predictors on the same scale: mean of zero and unit variance
my_lm = train(training[,1:4], training[,5],
method = "lm",
preProc = c("center", "scale")
)
message("Linear Regression: Model performance on \n the training set")
my_lm$results[c("RMSE","Rsquared")] %>%
round(2)
summary(my_lm)
Linear Regression: Model performance on
the training set
RMSE Rsquared
4.61 0.93
Call:
lm(formula = .outcome ~ ., data = dat)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-43.281 -3.164 -0.117 3.239 17.704
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 454.39620 0.05233 8683.725 < 2e-16 ***
AT -14.62996 0.12728 -114.943 < 2e-16 ***
V -3.03266 0.10347 -29.309 < 2e-16 ***
AP 0.39110 0.06320 6.189 6.38e-10 ***
RH -2.23520 0.06804 -32.849 < 2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
Residual standard error: 4.579 on 7651 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.9281, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9281
F-statistic: 2.469e+04 on 4 and 7651 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
Predict using the test data
pred = predict(my_lm, testing[, 1:4])
SSE = sum((testing[,5] -pred)^2) # sum of squared errors
SST = sum((testing[,5] - mean(training[,5]))^2) # total sum of squares, remember to use training data here
R_square = 1 - SSE/SST
message('R_squared on the test data:')
round(R_square, 2)
SSE = sum((testing[,5] - pred)^2)
RMSE = sqrt(SSE/length(pred))
message("Root mean square error on the test data: ")
round(RMSE, 2)
R_squared on the test data:
0.93
Root mean square error on the test data:
4.48
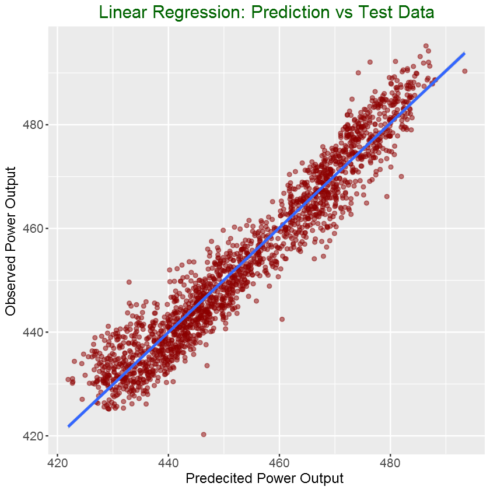
Preparing data for ploting
my_data = as.data.frame(cbind(predicted = pred,
observed = testing$PE))
# Plot predictions vs test data
ggplot(my_data,aes(predicted, observed)) +
geom_point(color = "darkred", alpha = 0.5) +
geom_smooth(method=lm)+ ggtitle('Linear Regression ') +
ggtitle("Linear Regression: Prediction vs Test Data") +
xlab("Predecited Power Output ") +
ylab("Observed Power Output") +
theme(plot.title = element_text(color="darkgreen",size=18,hjust = 0.5),
axis.text.y = element_text(size=12),
axis.text.x = element_text(size=12,hjust=.5),
axis.title.x = element_text(size=14),
axis.title.y = element_text(size=14))
This blog post series is on machine learning with R. In this first post, we saw non-regularized multivariate linear regression. In the second part of the post, we will work with regularized linear regression models. Next, we will see the other non-linear regression models. See you in the next post.