In this post, I will show how to collect data from a webpage and analyze or visualize in R. For this task I will use the rvest package and will get the data from Wikipedia. I got the idea to write this post from Fisseha Berhane.
I will gain access to the prevalence of obesity in the US from Wikipedia page, then I will plot it on the map. Let’s begin with loading the required packages.
## LOAD THE PACKAGES #### library(rvest) library(ggplot2) library(dplyr) library(scales)
Download the data from Wikipedia.
## LOAD THE DATA ####
obesity = read_html("https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obesity_in_the_United_States")
obesity = obesity %>%
html_nodes("table") %>%
.[[1]]%>%
html_table(fill=T)
The first line of code is calling the data from Wikipedia and the second line of codes is transforming the table that we are interested into a data frame in R.
The head of our data.
head(obesity) State and District of Columbia Obese adults Overweight (incl. obese) adults 1 Alabama 30.1% 65.4% 2 Alaska 27.3% 64.5% 3 Arizona 23.3% 59.5% 4 Arkansas 28.1% 64.7% 5 California 23.1% 59.4% 6 Colorado 21.0% 55.0% Obese children and adolescents Obesity rank 1 16.7% 3 2 11.1% 14 3 12.2% 40 4 16.4% 9 5 13.2% 41 6 9.9% 51
The data frame looks good, now we need to clean it from making ready to plot.
## CLEAN THE DATA ####
str(obesity)
# remove the % and make the data numeric
for(i in 2:4){
obesity[,i] = gsub("%", "", obesity[,i])
obesity[,i] = as.numeric(obesity[,i])
}
# check data again
str(obesity)
'data.frame': 51 obs. of 5 variables:
$ State and District of Columbia : chr "Alabama" "Alaska" "Arizona" "Arkansas" ...
$ Obese adults : chr "30.1%" "27.3%" "23.3%" "28.1%" ...
$ Overweight (incl. obese) adults: chr "65.4%" "64.5%" "59.5%" "64.7%" ...
$ Obese children and adolescents : chr "16.7%" "11.1%" "12.2%" "16.4%" ...
$ Obesity rank : int 3 14 40 9 41 51 49 43 22 39 ...
'data.frame': 51 obs. of 5 variables:
$ State and District of Columbia : chr "Alabama" "Alaska" "Arizona" "Arkansas" ...
$ Obese adults : num 30.1 27.3 23.3 28.1 23.1 21 20.8 22.1 25.9 23.3 ...
$ Overweight (incl. obese) adults: num 65.4 64.5 59.5 64.7 59.4 55 58.7 55 63.9 60.8 ...
$ Obese children and adolescents : num 16.7 11.1 12.2 16.4 13.2 9.9 12.3 14.8 22.8 14.4 ...
$ Obesity rank : int 3 14 40 9 41 51 49 43 22 39 ...
Fix the names of variables by removing the spaces.
names(obesity) names(obesity) = make.names(names(obesity)) names(obesity) [1] "State and District of Columbia" "Obese adults" [3] "Overweight (incl. obese) adults" "Obese children and adolescents" [5] "Obesity rank" [1] "State.and.District.of.Columbia" "Obese.adults" [3] "Overweight..incl..obese..adults" "Obese.children.and.adolescents" [5] "Obesity.rank"
Now, it’s time to load the map data.
# load the map data
states = map_data("state")
str(states)
'data.frame': 15537 obs. of 6 variables:
$ long : num -87.5 -87.5 -87.5 -87.5 -87.6 ...
$ lat : num 30.4 30.4 30.4 30.3 30.3 ...
$ group : num 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
$ order : int 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
$ region : chr "alabama" "alabama" "alabama" "alabama" ...
$ subregion: chr NA NA NA NA ...
Merge two datasets (obesity and states) by region, therefore we first need to create a new variable (region) in obesity dataset.
# create a new variable name for state obesity$region = tolower(obesity$State.and.District.of.Columbia)
Merge the datasets.
states = merge(states, obesity, by="region", all.x=T) str(states) 'data.frame': 15537 obs. of 11 variables: $ region : chr "alabama" "alabama" "alabama" "alabama" ... $ long : num -87.5 -87.5 -87.5 -87.5 -87.6 ... $ lat : num 30.4 30.4 30.4 30.3 30.3 ... $ group : num 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ... $ order : int 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ... $ subregion : chr NA NA NA NA ... $ State.and.District.of.Columbia : chr "Alabama" "Alabama" "Alabama" "Alabama" ... $ Obese.adults : num 30.1 30.1 30.1 30.1 30.1 30.1 30.1 30.1 30.1 30.1 ... $ Overweight..incl..obese..adults: num 65.4 65.4 65.4 65.4 65.4 65.4 65.4 65.4 65.4 65.4 ... $ Obese.children.and.adolescents : num 16.7 16.7 16.7 16.7 16.7 16.7 16.7 16.7 16.7 16.7 ... $ Obesity.rank : int 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ...
Plot the data
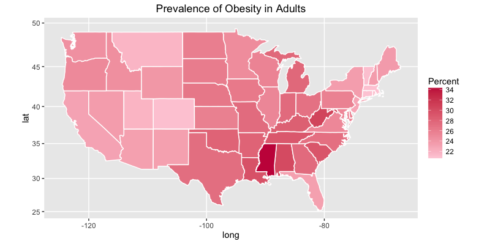
Finally we will plot the prevalence of obesity in adults.
## MAKE THE PLOT ####
# adults
ggplot(states, aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group, fill = Obese.adults)) +
geom_polygon(color = "white") +
scale_fill_gradient(name = "Percent", low = "#feceda", high = "#c81f49", guide = "colorbar", na.value="black", breaks = pretty_breaks(n = 5)) +
labs(title="Prevalence of Obesity in Adults") +
coord_map()
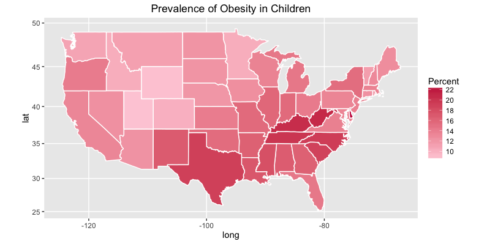
Similarly, we can plot the prevalence of obesity in children.
# children
ggplot(states, aes(x = long, y = lat, group = group, fill = Obese.children.and.adolescents)) +
geom_polygon(color = "white") +
scale_fill_gradient(name = "Percent", low = "#feceda", high = "#c81f49", guide = "colorbar", na.value="black", breaks = pretty_breaks(n = 5)) +
labs(title="Prevalence of Obesity in Children") +
coord_map()
If you like to show the name of State on the map use the code below to create a new dataset.
statenames = states %>%
group_by(region) %>%
summarise(
long = mean(range(long)),
lat = mean(range(lat)),
group = mean(group),
Obese.adults = mean(Obese.adults),
Obese.children.and.adolescents = mean(Obese.children.and.adolescents)
)
After you add this code to ggplot code above
geom_text(data=statenames, aes(x = long, y = lat, label = region), size=3)
That’s all. I hope you learned something useful today.